Creative Problem Solving
Approach a problem in an imaginative, innovative, and unconventional way
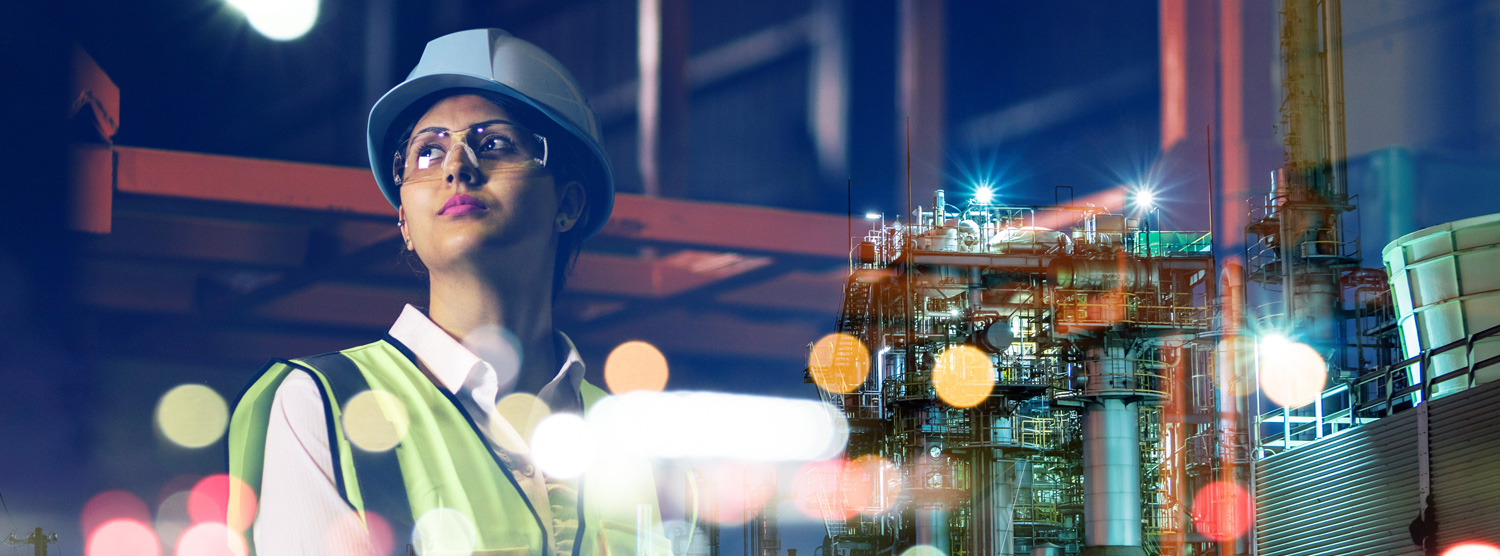
Our management approach in which all departments, employees, and managers become responsible for continuously improving quality so that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations. The Total Quality Control TQC methodology relies on the Plan, Do, Check, Adjust (PDCA) cycle to manage processes and, when problems arise, using statistical tools to solve them. The methodology and tools are used often by employees during kaizen activities and together form an important subsystem of Flow It Right.
Root Cause Analysis
Our root cause analysis helps to ensure that a problem is truly eliminated by applying corrective action to the “root cause” of the problem. Many different problem solving techniques have different names for the same basic activities. Therefore, we utilize an optimized subset of these tools that focuses on resolving the underlying problem instead of applying quick fixes that only treat immediate symptoms. Our common approach is to ask why five times, each time moving a step closer to discovering the true underlying problem.
Some Tools:
DMAIC
A3
PMCS
Quick Kaizen
Cause and Effect (Fishbone)
Five Whys
PDCA
TPM
PDCA
Plan, Do, Check, Adjust
The PDCA Cycle is a systematic series of steps for gaining valuable learning and knowledge for the continuous improvement of a product or process.
Plan: This involves identifying a goal or purpose, formulating a theory, defining success metrics, and putting a plan into action.
Do: The components of the plan are implemented, such as making a product.
Check: Outcomes are monitored to test the validity of the plan for signs of progress and success, or problems and areas for improvement.
Adjust: This step closes the cycle, integrating the learning generated by the entire process, which can be used to adjust the goal, change methods, or even reformulate a theory altogether.
These four steps are repeated over and over as part of a never ending cycle of continuous improvement.
Cause and Effect Diagram
Our visual problem solving tool is used to logically organize potential causes for a specific problem or effect by graphically displaying them in increasing detail. It helps to identify root causes and ensures mutual understanding of the causes.
Also known as a “Fishbone” or “Ishikawa” Diagram.
Cause and Effect Diagrams will help companies “drill down” to potential root causes:
- May show multiple root causes.
- May show a single root cause that recurs in multiple places.
Five Whys
A technique for discovering the root causes of a problem and showing the relationship of causes by repeatedly asking the question, “why?” The technique uses repetitive questioning to probe deeper to surface the root cause of a problem. The number of times “why” is asked depends on when the true root cause is reached but should be at least 3 “Whys” and not exceed 8 “Whys”.