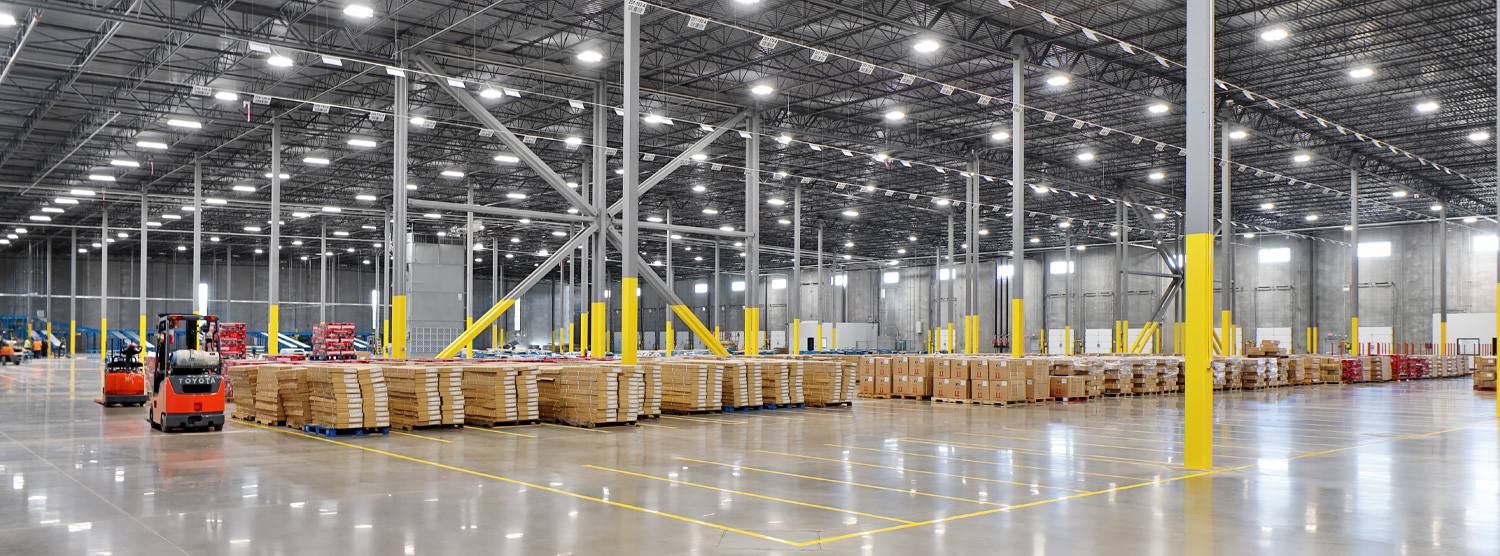
Standardized Operations
Operations that are done the same way, every time, regardless of who is doing them
We create standardized operations by establishing precise procedures for each operator’s work in a production process, leveraging:
- Takt time, which is the rate at which products must be made in a process to meet customer demand.
- The precise work sequence in which an operator performs tasks within Takt time.
- The standard inventory, including units in machines, required to keep the process operating smoothly.
The benefits of standardized operations include documentation of the current process for all shifts, reductions in variability, easier training of new operators, reductions in injuries and strain, and a baseline for improvement activities.
Standardized operations, once established will ensure your company is positioned to:
- Provide a safe work environment
- Keep high quality standards
- Identify waste within the process
- Provide a management tool to differentiate between normal and abnormal
- Build the Foundation for Continuous Improvement
Employees Safety and Security
All flows, layouts, workplace organization and process improvements we create, and implement are designed to strengthen employers’ and employees’ self reliance in dealing with occupational health and safety issues and thereby making workplaces safer.
Some items to consider:
- Available cleaning equipment
- Safety procedures
- Personal protective equipment
- Ergonomics
- Site safety equipment
- Fire exits/no drop zones
- Safety teams
- Safety committees
- Site maps
No one knows a workplace better than the people who work in it, so our partnership with the employees and employers are critical in identifying and resolving health and safety concerns. We ensure all employees have a key role to play in preventing work related injuries and diseases.
Poka Yoke
Our approach to “mistake proofing” in all aspects of manufacturing, customer service, procurement, etc. It employs visual signals that make mistakes clearly standout from the rest, or devices that stop an assembly line or process if a part or step is missed.
Theory of Constraints (TOC)
We will leverage Dr. Eliyahu Goldratt management philosophy and a set of tools for organizational change. TOC concentrates on improving profits by managing constraints, factors that prevent a company from achieving its goals. Its primary focus is on removing or managing constraints to improve throughput, while Lean focuses on the identification and removal of waste to improve the flow of value. Both Lean and TOC emphasize improving and standardizing the whole system rather than individual parts.